Resources and Development Notes For Class X Students
Resources and Development notes are essential for class X students. These notes will help you to understand the relation between resources and human development. Additionally. these notes cover topic like sustainable development, resource planning, development of resources, land use pattern in India and about the various types of soils. In these resources and development notes, we will also cover the important and expected questions asked from each topic. Therefore, these class notes are going to be very helpful to all the students of class X.
60 Most Expected Geography Questions In Term I From Class X
Resources and Development Notes For Class X Students
Definition of Resource
Everything which are available in our environment and can satisfy our needs provided it is technologically accessible, economically feasible (affordable) and culturally acceptable can be termed as resource.
Define Resource.
CLASS X GEOGRAPHY RESOURCES AND DEVELOPMENT NOTES
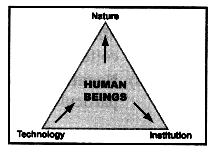
Interdependent Relationship Between Nature, Institution and Technology
Human beings interact with nature with the help of technology and create institutions to accelerate economic development.
Nature provides us with resources, and technology helps us establish laboratories and industries. However, in the absence of resources, technology, and institutions, they will be of no use.
what is the relationship between Human and Nature?
Are Resources Free Gifts Of Nature?
Many people consider resources to be free gifts of nature, but this is not true because resources are functions of human activities.
Resources require human effort and money to extract and use.
Classification of Resources
Resources can be classified based on
a) ORIGIN: Biotic & Abiotic
b) EXHAUSTIBILITY: Renewable and Nor-Renewable
c) OWNERSHIP: Individual, Community, National & International
d) STATUS OF DEVELOPMENT: Developed, Potential, Stock & Reserve
How are resources classified based on status of development?
Development of Resources (Why are resources not getting developed?
- Depletion of resources to satisfy the greed of a few individuals.
- Control of resources in few hands which divided the society into haves and have not.
- Blindly exploited resources which has caused Global warming, pollution, and Ozone layer depletion.
Why are resources not getting developed?
Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development means development should take place
i) without damaging the environment.
ii) use the resource in present and
iii) do not waste the resources so that future generations have sufficient for their use.
Define Sustainable Development.
Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit 1992
- First International Earth Summit held ai Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, South America.
- More than 100 countries participated.
- Major problems discussed were Environmental protection and Socio-Economic Development at the global level.
- All the leaders present signed the declaration of Global climatic change and Biological Diversity.
- Leaders agreed on Global Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 to achieve Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
Agenda 21
- A declaration was signed by the global leaders at ” United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in 1992.
- The summit aims to achieve Global Sustainable Development.
- It includes the elimination of poverty, environmental damage, and disease through shared responsibilities.
- The major objective was ” every local government should draw its own Agenda 21″.
What was the major aim and objective of Rio de Janeiro earth summit?
Resources and Development Notes For Class X Students
Resource Planning
Judicious use of resources to minimize damage and wastage is called Resource Planning.
Why Resource Planning in India?
India has enough resources but it is very unevenly distributed. Some areas have enough but few areas have acute shortages. For example:
- Jharkhand Chhattisgarh and Odisha are rich in coal and other minerals.
- Arunachal Pradesh is rich in water resources but lacks infrastructural development due to the hilly region.
- Rajasthan is rich in Solar and wind Energy but lacks water resources.
- Ladakh is rich in Cultural heritage but lacks water and other vital minerals.
Therefore, resource planning becomes essential at National, state, and at local levels for the all-round development of the country.
What is resource planning? Why is resource planning essential in India?
Three Stages of Resource Planning in India
- Identification of resource by surveying, mapping and checking the quality and quantity of resource.
- Making a planning structure in accordance with technology, skill and institutional set up.
- Matching the resource development plans with overall National Development Plan.
what are the three stages of resource planning?
Conservation of Resources
Resources must be conserved because:
i) Resources are limited.
ii) It takes millions of years in its formation,
iii) Many resources are non-renewable.
Mahatma Gandhi said, “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for anybody’s greed.” He placed greedy and selfish individuals and the exploitative nature of modern technology as the root cause for resource depletion at the global level. He was against mass production and wanted to replace it with the production of the masses.
What did Mahatma Gandhi say about resources? How can resources be conserved?
Land Resources
- The land is an important resource because it supports Natural vegetation, wildlife, Human life and economic activities, transportation etc.
- It is static means fixed and cannot be increased.
- Three types of land available in India are Mountains 30%. Plateaus 27% and Plains 43%.
Land Utilization
- Forests 33%
- Barren and wasteland
- Permanent pasture land
- Fallow land: Land left uncultivated for 1 to 5 years.
- Current Fallow Land: Land left uncultivated for less than 1 year.
- Culturable Fallow Land: Land left uncultivated for more than 5 years.
- Net Sown Area: It is the percentage of the country’s total land area used to grow crops.
- Gross Cropped Area: Total area is sown once and more than once in a particular year.
Define fallow land, Net Sown Area and Gross Cropped Area.
Land Use Pattern In India
- Total Geographical area of India – 3.28 million square kilometers.
- Land use data available is only 93%
- This is due to North Eastern states and Jammu & Kashmir data is not available due to disputed International borders.
- The pattern of the Net Sown Area varies greatly. In Punjab & Haryana, it is over 80% whereas in Arunachal it is less than 10 %.
Land Degradation & Conservation Measures
Causes of land Degradation: Human factors
- Mining sites are left after taking out minerals making land unfit for cultivation.
- Deforestation due to mining in Jharkhand, Odisha and Chhattisgarh causes land degradation.
- Land degradation in Rajasthan Gujarat and Maharashtra is due to Over Grazing.
- Water Logging (at one place) is responsible for land degradation in Punjab, Haryana and western U.P.
- Dumping of Industrial effluents on land also degrades the land.
Mention any 5 human factors that cause land degradation.
Conservation of land
- Afforestation
- Proper management of grazing.
- Planting of shelter belts
- Stabilization of dunes.
- Control over mining activities.
- proper management of wasteland.
- Proper treatment of Industrial wastes.
How can land degradation be controlled?
Resources and Development Notes For Class X Students
Soil as a Resource
Factors affecting soil formation are
- Forces of nature e.g. cyclones, earthquakes, volcanic eruption, flood etc.
- Chemical and organic changes.
Classification of soils
Alluvial soils
- are the most widely spread and important soil.
- Mostly found in the Northern plains and Eastern coastal regions where rivers make the delta.
- N. Three major rivers mainly form plains; Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra.
- According to the age alluvial soil can be classified as Khadar and Bangar soil.
- Khadar is new alluviam hence more fertile.
- Bangar is old alluvium, hence contains kankar nodules and is comparatively less fertile.
- Important crops that is grown is wheat, paddy Maize, etc.
Distinguish between Khadar and Bangar soil.
2. Black Soil
- Also known as Regur soil or Black cotton soil.
- Found in western peninsular India including major parts in Gujarat, Maharashtra, and western M.P.
- Two major reasons for its formation are the climatic conditions and the parent rock material.
- Develops deep cracks during summer.
- Has high water retaining capacity.
- Important crops that are grown are cotton, sugarcane, etc.
- rich in soil nutrients, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime.
Mention important features of Black soil.
3. Red & Yellow soil
- Mostly found at the Eastern borders and in the southern parts of Deccan plateau.
- It looks red due to the diffusion of iron.
- It looks yellow when in hydrated (wet) form.
4. Laterite Soil
- This soil develops under tropical and subtropical climate with alternate wet and dry season.
- These soils are very deep and acidic.
- Lack nutrients and found in patches.
- prone to erosion and degradation.
- Important crops that can grow are Tea, Coffee and Cashew Nut.
5. Arid Soil
- Also known as sandy soil.
- sandy in texture and saline in nature.
- Found in the regions of low rainfall.
- Soil is infertile and lacks humus and moisture.
- Found in w. Rajasthan
6. Montane & Forest Soils
- found in the hilly and mountainous areas
- are acidic with low humus content
Resources and Development Notes For Class X Students
Soil Erosion and Conservation
- The removal of the soil from one place to another by the forces of wind, water, etc. is known as soil erosion.
- The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies.
- The land becomes unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land.
- In the Chambal basin such lands are called ravines.
- washing away of the top layer of soil by water or wind is called sheet erosion
what is gully erosion? which river is responsible for gully erosion in India?
Soil Conservation Measures
- Contour Ploughing
- Terrace farming
- Shelter belts
- Strip cropping
- Minimizing the use of chemicals and fertilizers.
Describe any five methods of soil conservation?
Resources and Development Notes For Class X Students
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Resources and development notes for class X students will definitely help you in preparing for your board examination. All expected questions are also mentioned after each topic to prepare well. In the board examination, teachers may ask questions that assess students’ understanding of resource classification, renewable and non-renewable resources, factors affecting resource distribution, environmental degradation due to resource exploitation, and conservation measures.
I believe that these notes provide a comprehensive foundation for students of class X to tackle complex issues related to Resources and Development in their examinations.
Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 MCQs & Source Based Questions
11-Point Project On Consumer Awareness
Were these notes on Resources and Development helpful to you? Feel free to write your comment in the box given below. Your feedback will mean a lot to me.






0 Comments