History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When Lesson Plan
Class VI Social Science Lesson plan for the month of April-May 2022 is the road map for any teacher. Moreover, you are more focused if you have Class VI Social Science lesson plan at the beginning of the session. You can easily use teaching aids and conduct tests. Social science of class VI is based on concepts, therefore for better interaction with students, social science lesson plan is must. Many new teachers face problems in designing the Class VI Social Science lesson plan during their initial years.
Class VI History Chapter 2 Lesson Plan – As Per NCF
This post mainly deals with a detailed Class VI Social Science lesson plan.
Hope, Class VI Social science lesson plan helps all social science teachers teaching in class VI
Here, I have tried to include objective, specific objective, method of teaching, teaching aids, activities, home-work planned, learning outcome and remedial measures in my Class VI Social Science lesson plan.
For next Lesson Plan For the months of June-July, click on the given link. Class 6 Social Science Lesson Plan – Detailed, Interactive and Child Centric
History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When Lesson Plan
Topics covered:
- History Chapter 1. : What, Where, How and When
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 1. History: What, Where, How and When
General Objective:
Firstly, to develop students interest in the subject.
Secondly, to apply the knowledge practically in real life.
Thirdly, developing scientific temperament among the students.
Finally, to enhance student’s learning ability.
Specific Objective:
- Students will know the concepts of the past and periods of History.
- They will also know about the geographical framework of the earliest civilizations.
- Students will also learn about the sources of information used to study the past.
Checking Previous Knowledge:
At first, the teacher checks the previous knowledge of the students by asking a question.
We know what happened yesterday by watching T.V. news. But, how do we know what happened many years ago, in the past?
Introducing Topic:
At first, the teacher introduces the topic by asking basic questions like:
Teacher: Where do early men used to live?
Student’s response: Forests, Caves.
Teacher: On the banks of which river was the first civilization found?
Student’s answer: Sindhu river, Indus river, Indus valley civilization.
Teacher: Did people lived alone or in group near Indus river?
Student’s answer: Group.
Teacher: Where did the early people live?
Students are unable to answer this question.
Statement of Topic
O.K. So, today we are going to find out what people ate, the kind of clothes they wore, the sort of houses they lived and so on.
Introducing Topic: story telling method
Hunters and Gatherers
Do you know, thousands of years ago people lived along the banks of Narmada river.
These people were skilled gatherers. (people who gather their food)
Moreover, they were also knowing about the vast wealth of plants in the surrounding forests.
So, they collected fruits, roots from the forests for their food.
At times they also hunted animals.
So, they were also called hunters.
8000 years ago
Later, about 8000 years ago, they started growing wheat and Barley in North -West India.
Now people also began rearing animals like sheep, goat and dog.
They also started living in villages.
The Garo hills to the North east and the Vindhyas in central India were some of the other areas where agriculture first developed.
Rice was first grown to the North of Vindhyas.
4700 years ago
Then, about 4700 years ago, some of the earliest cities flourished on the banks of Indus river.
Later, about 2500 years ago, cities developed on the banks of the Ganga and its tributaries.
The area around Ganga and its tributary Son was known as Magadha.
Magadha rulers
Do you know, the rulers of Magadha were very powerful.
They set up a large kingdom.
Moreover, Kingdoms were also set up in in other parts of the Indian sub-continent.
Now, throughout people travelled from one part of the sub continent to another.
From Himalayas to deserts.
Rivers and seas made journeys dangerous at times but, never impossible.
So, men and women moved in search of livelihood.
Also, to escape from natural disasters like floods or droughts.
Sometimes, men marched in armies to conquer other lands.
India from Indus
The word India comes from the river Indus also called Sindhu in Sanskrit, Hind in Persian and Arabic.
The Iranians and the Greeks who came through the North west about 2500 years ago were also familiar with the Indus.
Moreover, they called the land east of Indus as India.
However, the name Bharat was used for a group of people who lived in the North west.
It is also mentioned in the Rigveda (the earliest composition in Sanskrit about 3500 years ago).
India and its neighboring countries together form the sub continent.
A sub continent is very large and is separated from the rest of Asia by seas, hills and mountains.
Finding out about the past

Manuscript: Hand written documents from class vi History Chapter 1. History: What, Where, How and When
There are many ways of finding out about the past.
One is to read books that were written long ago.
These are called manuscripts.
These were written on Palm leaves or on the specially prepared bark of a tree.
Many manuscripts were eaten away by the insects, some were destroyed but many have survived and preserved in temples.
These books deal with all kinds of subjects like religion, beliefs, faiths and practices.
Sometimes, kings got their orders inscribed so that people could see, read and obey them.
Often, kings kept records of victories in battle.
Besides, manuscripts and inscriptions, there were many other things that were made and used in the past.
Those who study these objects are called archaeologists.
They explore and excavate to find tools, weapons, pots, ornaments and coins.
Archeologists are like detectives who use all these sources like clues to find out about history.
What dates mean?
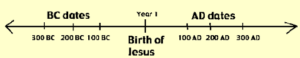
Dates are often written as AD and BC.
So, 20 B.C. means 20 years before the birth of Christ.
Where as 20 A D means 20 years after the birth of Christ.
Now a days CE (COMMON ERA) is used instead of AD and BCE (BEFORE COMMON ERA) is used instead of BC.
After listening to this story, the students will be curious to know more about the past.
Taking the advantage, the teacher starts explaining the chapter.
History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When Lesson Plan
Teaching aids:
Text Book, Black Board, Images and PPT
Technique:
Interactive with common examples.
However, the teacher uses various methods to make the topic interesting by interacting with the children in the class.
By asking very simple questions, the teacher draws the attention of the class.
Also make sure that the children are involved in the discussion.
While interacting with the students, the teacher also tells about different types of sources.
Later, The teacher also asks the students what all things you have at home to prove that you have passed class 1 five years back?
Answer: Books & notebooks, Fee receipt, old uniform, report card, class group photographs etc.
Content/ Teaching Points:
- What can we know about the past?
- Where did people live?
- Finding out about the past.
- One past or many
- What do dates mean?
First Activity:
Open Book Assessment
The teacher conducts an open book test.
To begin with, she Prepares 10 short questions from the chapter.
Students are asked to find out the answers from the text book and write in their copy.
Time: 30 minutes.
Second Activity
Imagine, You have to interview an archaeologist.
To begin with, prepare a list of five questions that you would like to ask her/him.
- What is Archaeology?
- What does an Archaeologist do?
- What is the process involved in excavation?
- How does Archaeologist determine the age of any of the objects discovered from excavations?
- Why are symbols important in the field of Archaeology?
Class work:
i) Firstly, Objective and short answer type questions will be done.
ii) Finally, Long answer type questions will be discussed and done in the class.
Home-work:
Draw or paste the pictures of different sources which are used by Historians.
Values imparted:
Firstly, Social responsibility of preserving our manuscripts and monuments.
Secondly, Sensitization towards keeping records.
Multidisciplinary Integrated learning:
- History: What were the advantages of settling near the river bank?
- Art: Draw a scene of early settlement?
- English: Write a paragraph on the topic “History is an important subject, even in the 21st century”
- Geography: Mark Greece, Iran, river Narmada, Indus and Ganga in the map.
Assessment Criteria:
Indicators
- Relevance of Content
- Presentation of information gathered
- Awareness of the information gathered
- Logical Approach
- Creativeness
- Analytical Skills
Learning Outcome:
After the completion of this chapter, students will be able to
- Firstly, explain the topic what Books and burial tell us.
- Secondly, discuss about source of History.
- Thirdly, sketch out the information we get from ancient sources and
- Finally, find facts about ancient History.
Remedial Measure:
Pair and share
Children sitting on the left side of the row will explain the chapter to the children sitting on their right.
For next Lesson Plan For the months of June-July, click on the given link. Class 6 Social Science Lesson Plan – Detailed, Interactive and Child Centric
History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When Lesson Plan
Conclusion:
I hope Social Science Lesson Plan of class VI will be of great help to the new teachers.
At last, I request you to comment and subscribe.
So that, you get the notification of the next lesson plan.
Was this lesson plan helpful to you? Write your views in the comment box.
For next Lesson Plan For the months of June-July, click on the given link.
Class 6 Social Science Lesson Plan – Detailed, Interactive and Child Centric






Excellent
Really helpful
Kindly post Class 4 Social Science lesson plans.
Kindly post the Oct, Nov ,Dec and Jan class Vl lesson plans
shapingminds.in
https://shapingminds.in › class-vi-so…
Class VI Social Science Lesson Plan For October – November
Sent. Pl. Check