The very first question is, why should you read NCERT Class VII Chapter 3 Our Changing Earth? Because there are many things which you probably do not know. The place where Himalayas exist was once occupied by the sea. The place where sea exists was once occupied by land. Do you know, India, Australia and South America was once connected with Africa. Surprised? Read about continental drift.
In this Chapter “Our Changing Earth”, we will read about the changing nature of the Earth and its causes. Now, you already know that nothing on the earth is static. But how does this form of the Earth change? What are the factors that change the earth? Today we will discuss all these in this article. To read this chapter in Hindi click हमारी बदलती पृथ्वी
NCERT CLASS VII GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER 3 OUR CHANGING EARTH
Movement of Lithosphere
There are some huge pieces of land above the earth.
We call these pieces the lithosphere.
Today, they are also far from each other.
Each big piece of land is known by different names like North America, South America, Africa, etc.
You will be surprised to know that these big pieces of land are floating like a ship.
What make these plates move?
There is hot molten magma inside the Earth.
It tries to come out all the time.
But due to the solid and thick lithosphere, it cannot come out.
Just like when we boil tea, it rises and try to come out of the vessel.
But when you reduce the temperature, it comes down but does not allow the tea to be stable.
In the same way, magma also does not allow the Lithosphere to remain stable at one place.
Therefore, it keeps moving a few millimeters every year.
Movement on the earth:
There are two types of movements.
One is inside and the other one is outside the earth.
Just like in your body, movement takes place inside and outside the body.
The forces which act in the interior of the earth is called the endogenic force.
and the forces which act on the surface (outside) of the earth, are called the exogenic force.
Endogenic force and our changing earth
Endogenous forces can also be of two types – sudden or gradual.
When there is a sudden force coming from inside the earth, no one can stop it.
It can cause volcano, earthquake or landslide.
Volcano: When nature celebrates Deepawali.

Sometimes there is so much force inside the earth that everything inside it comes out.
This is what we call a volcano.
This causes a big change on the earth suddenly.
Does this happen in your body also?
Do you have any control on vomiting?
No, due to disturbance inside the stomach, there is a force inside which is not in your control and you vomit.
Everything eaten comes out.
According to NCERT book ” A volcano is a vent (opening) in the earth’s crust through which molten material erupts suddenly.
Do you know that the Deccan plateau of India is not formed by a volcanic eruption. It is formed by fissure eruption.
Earthquake: When the earth gets heart attack (Heart quake)
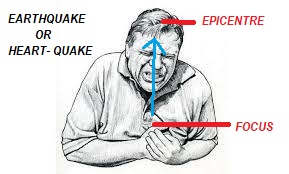
The part of the land above, after all, is also resting on something.
The rock or plate carrying the load for so many years, breaks one day.
As soon as it breaks, everything that rests on it suddenly starts moving.
This is called an earthquake.
According to NCERT book “when the Lithospheric plates move, the surface of the earth vibrates. The vibrations can travel all round the earth.
These vibrations are called earthquakes”.
a) Focus:
The place inside the earth where the plate breaks, is called focus.
b) Epicenter:
Just above the focus on the surface of the earth is the epicenter. Maximum damage takes place at the epicenter.
c) Seismograph:
The name of the instrument by which earthquake is measured.
d) Richter Scale:
It is a scale attached to seismograph which records the intensity of earthquake.
An earthquake of 5 or less is less dangerous, between 5 to 7 can be dangerous.
It can damage old buildings, boundary walls, bridges, huts.
Above 7 on Richter scale can be very severe. It can damage anything and everything.
LANDSLIDE: When one leg of the mountain slip
Sometimes, the weak part of the earth moves from its location due to vibrations inside the earth.
This often happens in hilly areas.
A part of the mountain suddenly collapses.
This is called landslide.
Children who played on the sand in childhood and built the temple of sand have seen this happening.
When someone runs very close to the temple, a part of temple collapses due to the vibration.
This is called landslide.
Exogenic Force and our changing earth
Till now we have read how the force inside the earth changes over the earth.
Now we will read what are the forces on the earth which bring change.
There are mainly two major factors above the Earth.
They are weathering and erosion.
Weathering:
It is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface by air, temperature, force of water, humans, animals etc.
Example: When a teacher writes on board with a chalk, the chalk breaks due to friction and the particles fall down.
Erosion:
In simple words, erosion is the moving of small particles from one place to another.
According to NCERT “Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind and ice“.
Weathering and erosion creates new landforms on the surface of the earth.
Work of a river and our changing earth
A river remains busy doing weathering and erosion throughout its life.
We can divide its life into three stages namely Childhood, mature and old age.
Childhood/young stage: Destructive River?
The melting of glaciers above the mountain creates a river.
Like a child, the river is pure, clean, innocent and moves slowly creeping forward.
As it falls from the mountains and makes a waterfall, river becomes young and powerful.
The river starts the destructive work.
Breaks down hard rocks and creates its own way crossing all barriers with its force.
Due to the force and height from where a river falls, creates “V” shape valley.
Mature stage: Sensible river?
A river is said to be in mature stage when the river leaves the mountain and flows into a flat plain.
Now his river starts to slow down.
Wherever a slight slope is found in the plains, the river twists and turn.
In this way the river flows like a snake.
This “S” shape flow of river is called the Meander.
Continuous erosion and deposition work is carried out on the edges of Meander.
This cause erosion loops to cut from the main river forming an Ox-Bow lake.
During the rainy days, due to excessive water, the river breaks its two sides and widens itself.
The river spreads the soil on its banks far and wide.
When the flood water decreases, the river recedes back to its bed, leaving the soil.
This is known as floodplains.
Old age: Helpless river.

As the river progresses through the plains, it starts to get old.
The river becomes weak.
Now there is neither the strength to break the rocks nor to carry away the soil with it.
How so ever small particles are in the river, the river dumps it.
Due to deposition on its own way, the path of the river gets blocked.
The river then is distributed into thousands of channels called distributaries. (like the branches of trees.)
One such thin branch of Ganga is the Hooghly River in Calcutta.
The river spreads into many branches in a triangular shape before meeting the sea.
A triangular piece of fertile land, formed by a river, before falling into the sea is called Delta.
Then the river merges into the sea and the river ends.
The work of sea waves and our changing earth
Both erosion and deposition occur due to the continuous rise of waves in the sea and hitting the coast.
Continuous waves collide with the big rocks present in the sea, which makes it rough.
You will not find anything smooth on the seashore.
Cracks occur as they become rough.
Over time the crack increases and widens into what is called a sea cave.
Gradually, this cave becomes so large that it can be passed through it.
It is called coastal arch.
Continuous erosion also breaks the roof over time, causing the rock to split into two separate parts.
This wall like feature is called stacks.
Continuous waves hit the coast and make it even wider, creating sea beach.
Work of Ice (Glacier)
If you move a heavy box from a pile of sand, what will you see?
You will see small sand hills on both the sides with a scratched bottom.
That is, the way the box is routed will appear “U” shaped.
Similarly, the glacier over mountains is heavy and breaks.
Due to the slope on the mountains, it starts to slide slowly.
Wearing and tearing both the side and the bottom of the hill.
The place where the pieces of stone, sand and soil is deposited, is called glacial moraines.
When the glacier comes down through the slopes, it starts melting due to heat.
When it continues for many years, the distance between two hills increases and deepens.
Thus, “U” shape valley is formed.
Work of wind and our changing earth

A vast area filled with sand is called a desert.
It is an open space where wind mainly performs erosion and deposition work.
Umbrella or Mushroom-shaped rocks appear in the desert.
Do you know why?
Note: Due to sand in the desert, the daytime temperature is high because the sand gets heated quickly. At sunset, the temperature of the desert starts decreasing rapidly because the sand also cools rapidly.
Formation of Mushroom rocks: Umbrella in the desert
In the desert, due to extreme heat during the day, the outer shell of rocks expands.
At night, due to extreme cold. the rock shrinks.
Thus, the outer part of the rock becomes loose and weak.
Due to continuous expansion and shrinking, the outer cover of the rock becomes loose.
When the wind blows, heavy sand particles hit the bottom part of the rock.
Lighter particles hit the upper part of the rock.
Because of this the rock breaks more from the bottom and less at the top.
This makes the lower part of the rock narrow and the upper part wide.
Sand Dunes
Sand particles are finer and lighter.
When the air moves, it carries the lighter particles.
When the speed of the wind decrease, the sand particles get accumulated at one place.
This creates small mounds (hills) of sand which is called sand dunes.
Formation of Loess
When air takes away the light particles of sand and spreads it over a wide area, it is called Loess.
Large loess deposits are found in the deserts of Rajasthan in India and in China.
NCERT CLASS VII GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER 3 OUR CHANGING EARTH
Difficult words
Plate:
A solid layer of 5 to 200 km thickness formed from the upper layer of crust and upper mantle is called plate.
Erosion:
It is a natural process in which the particles of rock (loose material) is carried away by wind, water, or snow.
Deposition:
The settlement of loose particles at one place.
Internal force:
The internal forces drive all the vertical and horizontal movements of Earth’s crust and are responsible for some severe disasters such as earthquakes or volcanic eruption.
External force:
Force which act of the surface of the earth causing a change in the nature and shape of a landform.
Weathering:
It is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface by air, temperature, force of water, humans, animals etc.
Water Fall:
When the water of the river falls down from a steep gradient, it is called a water fall.
Meanders:
A meander is a “S” shape bend in a river channel. It only occur on the flat land.





0 Comments