Facts About Ocean Currents of the World For Competitive Exams
Know Everything About Ocean Currents For Competitive Exams in this article. Ocean Currents are nothing but the flow of water in the oceans. As the earth rotates and the wind blows so it is obvious that the ocean water cannot remain at one place. It is bound to move from one place to another. Moreover, the temperature on different parts of earth is also not the same. For example, places near the equator are hot and places near the poles are cold. This also makes the ocean water hot and cold which leads to the movement of water in the oceans known as currents.
What are Ocean Currents?
These are actually the horizontal and vertical circulation of water.
It is produced by the gravity, friction of wind and variation in the density of water at different parts of the Ocean.
Why are they Important?
1. They help in moving heat from equator to poles.
2. Movement of warm and cold ocean currents also affect the climate of a place.
3. Places where warm and cold ocean currents meet, provide favorable conditions for fishing.
4. Ocean currents protect our earth from Global Warming.
5. It also produces over half of world’s oxygen and absorbs fifty times more Carbon di oxide than the atmosphere.
6. Moreover, it also helps in transportation and sea life.
What are the effects of Ocean currents?
1. Ocean current results in rain.
2. They are also responsible for creating deserts.
3. It can support of destroy marine life.
What are the different types of Currents?
There are mainly two types of Ocean currents.
They are – Warm and Cold currents.
i) Warm Currents:
As the sun’s rays directly fall on equator, places near the equator become hot.
It also makes the air present over the equator hot.
Hot air is light and it rises up.
So, the winds from the nearby regions blow to fill the gap.
Fast movement of these winds pushes the sea water which ultimately makes the sea water move.
Therefore, warm ocean currents originate near the equator and move towards the poles.
ii) Cold Currents:
The sun’s rays fall slanting on the poles.
This makes the polar regions extremely cold.
This also makes the air cold.
As the cold air is dense and heavy they move toward the sub-polar regions.
Fast movement of these winds pushes the sea water.
Therefore, cold ocean currents originate near the poles and move towards the equator.
What is the difference between Waves, Tides and Ocean Currents?
The term Waves, tides and ocean currents seems to be same but all three are different.
Waves:
Waves are actually caused by the surface winds.
They are influenced by the force of winds.
For example, Take a plate filled with water and blow air.
The movement of water which you will notice are the waves.
Tides:
Tides are mainly caused by the gravity of sun, moon and earth.
Suppose the sun is shining brightly over India at 12 noon, so because of the gravitational force of the sun, it will pull the ocean water.
At this time there will be high tide in India and low tide on the opposite side of the globe.
For example
take a plate filled with water.
Now, slightly lift the plate from one side. What do you notice?
You will notice that the whole lot of water increases on one side and decreases on the other.
The place where the water (sea) expands, is known as high tide.
On the other hand the place where the water decreases, is known as low tide.
Ocean Currents:
Ocean currents are caused by the difference in temperature on the earth.
Equatorial regions are generally hot and polar regions are cold..
This difference in ocean water temperature causes movement of ocean water.
This is known as Ocean water currents.
Five Major Currents:
As you know that the ocean currents are caused by Global winds.
These winds drag the ocean water in the direction in which they blow.
As these currents reach the North Pole, they turn to their right due to Coriolis effect.
Similarly when they reach near the South Pole , they turn to their left.
In this way these currents move in a circular path from equator to the poles.
This spiral movement of water currents in the oceans are known as Gyres Class IX Term II Climate: How to write short answers in points?.
The five major ocean currents are:
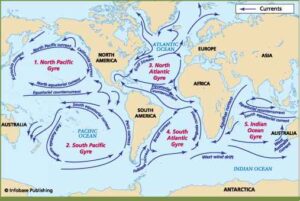
Five major ocean currents courtesy: Brian Williams
i) The North Atlantic ocean current:
Trade winds which blow near equator from west Africa is warm.
These winds drag the ocean water to the Gulf of Mexico.
As it reaches near the Caribbean sea, the current narrows and gain strength.
Further, these currents move along the eastern Coast of North America.
As it reaches near the north pole these ocean water currents become cold and moves under water and turn to their right.
From western Europe to North West Africa, these ocean currents move as cold currents.
When they reach near equator, they become warm again.
In this way this spiral movement is known as North Atlantic Gyre
ii) The South Atlantic Ocean:
In the southern hemisphere, near the equator the winds blow from South east.
These hot winds drag the ocean water from central western Africa towards South America.
When they reach to the eastern parts of South America, they turn to their south.
These warm ocean currents bring heavy rain in the eastern coast of south America.
When they reach near the south pole, these ocean currents become cold and turn to their left due to Coriolis force.
Now, these cold currents move along the west coast of Africa towards the equator.
As it proceeds towards equator, once again they become warm.
In this way this spiral movement is known as South Atlantic Gyre .
iii) North Pacific Currents:
The North Pacific currents flow from equator to 50 degree North latitude.
It forms one of the largest ecosystems.
These currents are governed by four prevailing currents.
All these currents move in clockwise direction.
The North Pacific current turn to the east to meet the California current.
The California current move to the south to meet the North equatorial current.
Lastly, the North equatorial current move west and reaches the eastern coast of Japan to meet the Kuroshio current.
Kuroshio current move towards North to meet the North Pacific Ocean Currents .
In this way the circle (Gyre) gets completed.
iv) South Pacific Currents:
We know that ocean water near equator becomes warm.
Therefore, south Pacific currents move west towards Australia.
These are the warm ocean currents. As they turn South from Australia,
they meet the cold Antarctic current.
Due to the lack of landmass (continents) these currents move freely in the south Pacific.
After meeting he cold Antarctic current, it proceeds towards the west coast of South America.
As these currents are cold, they do not cause any rainfall on the western coast of South America.
This circular movement of current is known as south Pacific Gyre.
v) The Indian Ocean:
The Indian ocean is the least explored oceans.
The warm currents flow towards the west and reaches to the eastern part of Africa.
There it turns south and move towards the west Australia.
From west Australia it turns towards equator to complete the cycle.
It is the warmest ocean EL-NINO, LA-NINA AND INDIAN MONSOON .
The most interesting feature of Indian ocean current is it reverses its direction during a year for some time.





0 Comments