Class IX Geography Chapter 1 – India- Size and Location:
Class IX Geography chapter 1 India – size and location is an important chapter.. https://www.jagranjosh.com/articles/ncert-geography-textbook-class-9-social-science-1589465950-1-geography-textbook-class-9-social-science-1589465950-1
Though, the chapter is smaller in length, but contains some very important concepts. It covers the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India, it’s size and location on globe, importance of India’s location at the head of Indian ocean along with the standard meridian of India. For better understanding of the chapter India- size and location, simple language has been used here. https://shapingminds.in/class-ix-geograp…d-ntse-questions/ All types of questions and answers including time calculation has been covered for better understanding.
TOPICS COVERED: INDIA- SIZE AND LOCATION
- INDIA’S LOCATION
- IT’S SIZE
- INDIA AND THE WORLD
- IT’S NEIGHBOURS
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
After completing the lesson students will be able to:
- Explain the implication of location of India & its vast size.
- Identify & locate standard meridian of India, Tropic of cancer & neighbouring countries.
- Define the concept of subcontinent & is able to identify countries part of Indian sub-continent.
- differentiate between latitudes & longitudes.
IMPORTANT TERMS:
PENINSULA: an area of land surrounded by water on three sides.
SUBCONTINENT: a subcontinent is part of a continent but is considered geographically as an independent entity.
STRAIT: A strait is a narrow body of water that connects two larger bodies of water
e.g. Palk strait connects Indian ocean with Bay of Bengal.
GULF: A gulf is a portion of the sea that penetrates (inserts) into land.
BAY: A bay is a body of water partially surrounded by land.
A bay is wider and less enclosed than a gulf.
Class IX Geography Chapter 1 – India- Size and Location:
INDIA’S LOCATION:
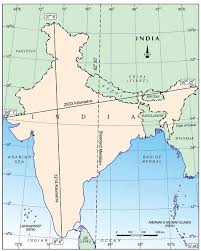
INDIA- SIZE AND LOCATION ( COURTESY CLASS IX NCERT )
- INDIA ENTIRELY LIES IN THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE.
- LATITUDINAL EXTENT: 8°4’ N TO 37°6’ NORTH
- LONGITUDINAL EXTENT:68°7’ E TO 97°25’ EAST
INDIA’S SIZE:
- Covering an area of 3.28 million square kilometres.
- India’s total area is 2.4% of the total geographical area of the world.
- India is the world’s seventh largest country
- India’s latitudinal and longitudinal extent is about 30 degrees.
- India’s standard time is based on 82°30’EAST , which passes near Mirzapur in UP.
- East-West extension – 2933 km
- North-South extension – 3214 km
- Land boundary _ 15,200 km
- Coastline length = 7500 km
TIME CALCULATION:
0° longitudinal line is called Prime Meridian.
Earth completes one rotation on its axis in 24 hours and in the process turns a complete circle of 360°.
This means Earth rotates 360° Divided by 24 Hrs. = 15° in one hour.
Difference of time for 15° longitude = one hour.
Difference of time for 1° longitude = 4 minutes.
EXAMPLE 1.
- Calculate the time at 5° E longitude when it is 9 a.m. at 35° E longitude ?
Ans. Time given at longitude = 35° E
Time asked at longitude = 5° E
Difference in longitude = 35° – 5° = 30° (difference between given and asked longitudes,
we know that, Difference between two longitudes = 4 minutes
Difference of time for 30° longitude Multiplied by 4 = 120 minutes = 2 Hours.
AS 5° E Longitude lies to the west of 35°E longitude,
Therefore,
2 hours will be subtracted from the given time i.e. 9.00 a.m.
So, the answer will be 7:00 am.
SOLVED EXAMPLE II :
Q 1. IF THE TIME AT 0° LONGITUDE IS 8:00 A.M. WHAT WILL BE THE TIME AT 22° EAST LONGITUDE?
SOLUTION
TIME GIVEN AT LONGITUDE = 0°
TIME ASKED AT LONGITUDE = 22°E
DIFFERENCE = 22-0 =22
WE KNOW THAT TIME DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TWO
LONGITUDES = 4 MINUTES. THEREFORE,
22 X 4 = 88 MINUTES i.e. 1 HOUR AND 28 MINUTES.
SO THE TIME DIFFERENCE WILL BE OF 1 HOUR AND 28 MINUTES.
AS THE TIME ASKED AT LONGITUDE IS TOWARDS THE EAST, THEREFORE,
1 HOUR AND 28 MINUTES WILL BE ADDED TO THE GIVEN TIME 8:00 A,M
ANSWER WILL BE 8:00 AM + 1 HOUR 28 MIN= 9: 28 HOURS
Class IX Geography Chapter 1 – India- Size and Location:
INDIA AND THE WORLD :
The Indian landmass is centrally located between West and East Asia.
The trans Indian ocean routes connect countries in the west and counties in the east.
India’s protruding Deccan Peninsula helped India to establish close contacts with West Asia, Africa and Europe, South-east and East Asia.
India is the only nation which has an ocean named after it.
India has contributed a lot to the world in forms of ideas, philosophies (Upanishads, Ramayana, Panchtantra) and mathematics (Indian numerals and decimal system).
Class IX Geography Chapter 1 – India- Size and Location:
INDIA’S NEIGHBOURS:
- Pakistan and Afghanistan in the northwest
- China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan in the north
- Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east
TWO ISLAND COUNTRIES WHICH DO NOT TOUCH THE BORDERS OF INDIA BUT ARE OUR NEIGHBOURS
Sri Lanka and Maldives
ACTIVITY – 1 : FROG RACE
Integrating Geography with Games and Mathematics

INDIA – SIZE AND LOCATION : INTEGRARING WITH GAMES AND MATHEMATICS.
Purpose : To make the students understand the last point of India and last point of the mainland of India.
Two frogs A and B start a race from the equator. In their first jump they reach up to 1° 4′ N Latitude, Second jump 2° 4′ N Latitude, Third jump 3° 4′ N Latitude and so on. Finally in their tenth jump they reach up to 10° 4′ N Latitude. Now, answer the following questions.
i) Out of all the ten jumps, which jump was the longest?
ii) Which frog will touch the southern most part of the mainland of India and in how many jumps?
iii) Will both the frogs be in water after their sixth jump? Where will they be?
IV) Which frog will reach Indira Point and in how many jumps?
V) If the finishing point is at 8° 4′ N Latitude. Which frog will reach there first.
Answers given at the end. Match your answers.
—————————————————————————————————————
Class IX Geography Chapter 1 – India- Size and Location:
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1 The southernmost point of the Indian union which got submerged under the sea water in 2004 during Tsunami is
a) Lakshadweep
b) Cape Comorin
c) Indira point
d) Kavaratti.
2. Opening of which canal reduced India’s distance from Europe by 7000 Km?
a) Indira Gandhi canal.
b) Suez canal
c) Gulf of Mannar
d) English channel.
3. What separates India from Sri Lanka.
a) Palk strait.
b) Gulf of Kutchch
c) Equator.
d) Tamilnadu.
4. Maldives islands are situated to the south of the _______________islands.
a) Lakshdweep
b) Andaman and Nicobar
c) Sri Lanka
d) Kerala
5. Which country is not the part of the Indian subcontinent?
a) Nepal
b) Bhutan
c) China
d) Maldives
6. India is called a subcontinent because of
a) it’s vast size.
b) it’s distinct culture.
c) physical features
d) all of these.
7. A peninsula is a piece of land that is bordered by water from __________________sides.
a) three sides.
b) all the sides.
c) Northern
d) Southern
8. The Tropic of cancer passes through how many states?
a) six
b) seven
c) eight
d) nine
9. Which neighbouring country will you reach if you sail across the Palk Strait.
a) Nepal
b) Bangladesh
c) Maldives
d) Sri Lanka
10. Which of the following is the oldest route of contact between India and other countries of the world?
a) Land routes
b) Ocean routes
c) rivers
d) Himalayan pass
QUESTIONS ASKED IN COMPETITIVE EXAMS (HOTS QUESTIONS)
11. Which geographical feature bounds India’s mainland south of 22°N Latitude?
a) Desert
b) Mountains
c) Plateaus
d) sea and oceans
12. Uttrakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West-Bengal and Sikkim has common frontiers with
a) Nepal
b) Bhutan
c) China
d) Bangladesh
13.Which of the following countries share the borders with India? ( UPSC)
1) Bhutan
2) Bangladesh
3) Thailand
4) Myanmar
Option
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1.2.and 4 only
D) All of the above
14. A narrow channel of sea separating two land masses is called: (NTSE)
a) Coastline
b) strait
c) Delta
d) Bay
15. Consider the following statements regarding the landmass of India? (UPSC & NTSE)
- The landmass of India has an area of 3.28 million square Km
- India’s total area accounts for 2.4 % of the total geographical area of the world.
Identify the correct statements:
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) All are correct
D) None
NCERT TEXT BOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS:
1. The sun rises two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat in the west but the watches show the same time. How does this happen?
Ans) i) The westernmost part of Gujarat lies at 68°7′ E Longitude.
ii) The Easternmost part of Arunachal Pradesh lies at 97°25′ E Longitude.
Difference between westernmost and easternmost Longitude is approximately 30 ( 30 x 4 =120 min or 2 hrs.)
Therefore, to have uniform time in the country, time of standard meridian 82°30′ E is followed.
As Gujarat and Arunachal Pradesh also follow the Indian Standard Time, watches show the same time.
2. The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance. Why?
Ans) central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance because:
i) The Indian landmass has a central location between the East and West Asia.
ii) The Trans-Indian Ocean routes, which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia, provide an important central location to India.
iii) The long coastline of India, thus helps India to establish close contact with East-West Asia, Africa and Europe.
iv) No other country has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean as India has.
v) it is India’s eminent position in the Indian Ocean, which justifies the naming of an Ocean after it.
EXTRA QUESTIONS:
Q1. Why is 82°30’E selected as the standard meridian of India ?
Ans) 82°30’E longitude is selected as the standard meridian of India because of the following reasons:
i) There is a general understanding among the countries of the world to select a meridian which is divisible by 7.5 (7°30′)
ii) Another consideration is that, the central meridian should pass through the middle of the country.
Q2. Why is the difference between the duration of day and night hardly felt at Kanyakumari but not so in Kashmir?
Ans) Difference between the duration of day and night hardly felt at Kanyakumari but not so in Kashmir because:
i) The days and nights are of same duration at the equator.
ii) As we move away from the equator, the variations in the day and night becomes greater.
iii) As Kanyakumari is quite near the equator and Kashmir far from the equator,
the day night difference is hardly felt there.
MAP- WORK FOR PRACTICE:
In an outline map of India, mark each of the following:
i) An island group which lies in Arabian sea.
ii) Indian standard meridian.
iii) Gulf of Mannar
iv) Palk Strait.
v) Easternmost and southernmost state of India.
vi) Tropic of cancer.
ANSWERS OF FROG RACE ACTIVITY:
i) First Jump ii) Frog A in eight jumps iii) No, Frog A will be in water, frog B at Indira Point. iv) Frog B in six jumps v) Both.
FOR NOTES, QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS, INTERESTING FACTS AND CONCEPTS RELATED TO GEOGRAPHY, VISIT REGULARLY.
SHARE AND SUBSCRIBE.




0 Comments