Solve 60 Most Expected Geography Questions In Term I In 60 Minutes From Class X
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for Revision for Class X board aspirants. If your Geography Revision of class X done, you can check your preparation by solving 60 most expected Geography questions. You will get an idea as well as practice by solving 60 most expected Geography questions before the Term I board exams. So, pick up pen and paper and start solving MCQ’s. Be honest to yourself while solving the questions. Solve all 60 most expected Geography questions in 60 minutes) http://cbseacademic.nic.in/sqp_classx_2021-22.html. Ready for the challenge. Let’s get started.
This article contains:
- Multiple Choice Questions from each chapter.
- Fill in the blanks
- Assertion and Reason based questions.
- Picture Based Questions
- Source Based Questions and
- Map Based Multiple Choice Questions.
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for Revision
Multiple Choice Questions:
01. Which one of the following is not a biotic resource?
(a) Soil
(b) Petroleum
(c) Coal
(d) Forests
02. Which of the following is not classified on the basis of status of development?
(a) Potential resource
(b) Developed resource,
(c) Renewable resource
(d) Stock and Reserves
03. Fill in the blanks with correct option.

Geography Revision Class X Term 1 – Image courtesy NCERT
OPTIONS:
(a) Nation
(b) Machines
(c) Technology
(d) None of the above.
04. If the resources are found beyond 200 nautical miles in the ocean, it is classified under which zone?
(a) Exclusive Economic Zone
(b) National Oceanic Zone
(c) Special Economic Zone
(d) Oceanic economic zone
05. The territorial waters that extend up to 12 nautical miles from the coast of a country is ____________ resource.
(a) National resource
(b) International resource
(c) Exclusive economic zone
(d) Oceanic resource
06. Which of the following is essential for sustainable existence of all forms of life?
(a) Resource extraction
(b) Resource management
(c) Resource planning
(d) Resource generation
07. Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as
(a) Fallow land
(b) Gross cropped area
(c) Net sown area
(d) Arable land
08. Which state among the North-Eastern states has been fully surveyed for its land use?
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Manipur
(c) Tripura
(d) Assam
09. Which of the following soil is more common in piedmont plains such as Duars, Chos and Terai?
(a) Black soil
(b) Laterite soil
(c) Alluvial soil
(d) Red soil
10. Which soil is also known as Regur soil?
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Red soil
(c) Black soil
(d) Laterite soil
11. Black soils are generally poor in
(a) Phosphoric content
(b) Moisture
(c) Potash
(d) Calcium carbonate
12. The red soil appears red due to the presence of:
(a) Potash
(b) Iron
(c) Phosphorous
(d) Humus
13. Laterite soil is mainly found in
(a) Western Rajasthan
(b) Western Ghats
(c) Eastern coastal plains
(d) Regions with low rainfall.
14. The lower horizons of the arid soil is occupied by kankar due to increasing
(a) Phosphorous content
(b) Potash content
(c) Lime, potash and phosphorous content
(d) Calcium content.
15. In the snow covered areas of Himalayas, which of the following soil experiences denudation and is acidic in nature with humus content?
(a) Laterite soil
(b) Black soil
(c) Alluvial soil
(d) Forest soil
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision is the most trending thing now?
16………. soils are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature.
(a) Laterite soil
(b) Arid soil
(c) Red soil
(d) Alluvial soil
17. The land becomes unfit for cultivation is known as……….
(a) Fallow land
(b) Bad land
(c) Deserted land
(d) Waste land
18. The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as _____?
(a) valleys
(b) gullies
(c) deltas
(d) estuaries
19. Identify the correct reason for the formation of gullies in bad lands.
(a) Formed when running water cuts through soils making deep channels.
(b) When water flows over large areas down a slope.
(c) When moving wind blows away loose soil of flat lands.
(d) Formed when ploughing is done in a wrong way.
20 …… is a strip cropping
(a) Planting two different crops.
(b) Planting cash crops
(c) Planting trees in a line
(d) Cultivating making steps
21. Complete the following table with correct information with regard to laterite soil
Soil | Soil texture | Areas where found | Crops grown |
Laterite soil | Loamy and Silty | _____________________ | Cashewnut & Tapioca |
(a) Low temperature and high rainfall
(b) High temperature and high rainfall
(c) High temperature and low rainfall
(d) Low temperature and low rainfall
(d) Plateau, low
22. Which of the following pair is not correctly matched?
(a) Alluvial soil- ideal for sugarcane
(b) Black soll- cotton
(c) Laterite sol- Tapioca
(d) Red soil – Wheat
23. Which one of the following pair is correctly matched?
(a) Biotic Resource – Petroleum
(b) Abiotic Resource-Forests
(c) Renewable Resource-Iron ore
(d) Non-renewable Resource – Iron
24. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) Sheet erosion – Top soil is washed away
(b) Wind erosion – wind blows loose soil of flat land
(c) Land not available for cultivation – arable land
(d) Soil ideal for cotton – Regur soil
Q25. The process of transformation of things available in our environment involves an interactive relationship between ………………………………………… ?
A. Nature and technology
B. nature, technology and institutions
C. Environment and nature
D. Environment and technology
Q26. How are resources classified?
A. On the basis of origin
B. On the basis of utility
C. On the basis of distribution
D. On the basis of potential
Q27. Give examples of National resources?
A. plots, houses
B. public parks, playgrounds, grazing grounds, burial grounds
C. oceanic resources
D. land, minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife
Q28. What are potential resources?
A. resources which can be renewed or reproduced
B. Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised
C. Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation
D. those things which are composed of non-living things
Q29. What are developed resources?
A. Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation
B. resources which can be renewed or reproduced
C. those things which are composed of non-living things
D. Resources which are found in a region, but we do not have the technology to use.
Q30. What is stock?
A. resources which can be renewed or reproduced
B. Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised
C. Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access these
D. solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife
Q 31. Fallow Land is _____________?
A. Land left uncultivated for 2-3 years.
B. land on which farming is done from 2-3 years.
C. Land put to non-agricultural uses
D. Net sown area and gross cropped area.
Q 32. What is the total geographical area of India?
A. 3.52 million sq km
B. 3.82 million sq km
C. 3. 48 million sq km
D. 3. 28 million sq km
Q 33. Waste land includes………………………
A. Land left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year
B. Land put to non-agricultural uses
C. rocky, arid and desert areas
D. Land left uncultivated for the past 1 to 5 agricultural years
Q34 What type of a resource are rocks?
A. Abiotic
B. Renewable
C. Potential
D. Biotic
Q35. Strip cropping prevents_____________ .
A. soil fertility.
B. erosion from wind.
C. erosion from the force of water
D. all of these.
Q36. Water in the dams and forests etc. is a ………….. resource which can be used in the future with the available technology?
A. Potential
B. Reserve
C. Stock
D. Developed
Q37. What are shelter belts?
A. Cultivating making steps
B. Planting lines of trees to create shelter
C. Planting huge bush plants in deserts
D. Planting near water bodies.
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision
PICTURE BASED QUESTIONS FOR GEOGRAPHY REVISION CLASS X
Q 38. Identify the personality from the given clues.
i) He participated in Satyagraha as one of the foremost satyagrahis.
ii) He was one of the votaries of Gandhi’s concept of Gram Swarajya.
iii) initiated Bhoodan and Gramdan movement.

Geography Revision Class X Term I Courtesy image : Quote Tab
A. Acharya Vinoba Bhave
B. Baba Amte
C. Kailash Satyarthi
D. Medha Patkar
Q39.. Which type of erosion is depicted in the picture given below?

a) Sheet erosion
(b) Glacial erosion
(c) Gully erosion
(d) Wind erosion
Q40. Identify the soil which develop deep cracks during dry spells?

A. Red soil
B. Regur soil
C. Arid soil
D. Alluvial soil
Q41. Look at the image and identify the method of soil conservation?

(a) Strip cropping
(b) Shelter belt
(c) Terrace farming
(d) Afforestation
42. Match the following.
List A | List B |
A. Laterite soil | 1. High moisture retention |
B. Black soil | 2. Intensively cultivated |
C. Alluvial soil | 3. Source of salt |
D. Arid soil | 4. Formed by leaching |
A B C D
(a) 1 4 2 3
(b) 4 2 3 1
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 2 4 3 1
43. Match the following.
List A | List B |
A. Coal | 1. National resources |
B. Burial Grounds | 2. Biotic |
C. Railways | 3. Community owned resources |
D. Forests | 4. Renewable resource |
A B C D
(a) 2 3 1 4
(b) 3 2 4 1
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 2 4 3 1
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision
ASSERTION AND REASON BASED QUESTIONS
Directions: In the given question, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct code.
44. Assertion (A): The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion.
Reason (R): Soil erosion takes place only in hilly regions.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
45. Assertion (A) The lower horizon of the arid soil is occupied by kankar.
Reason (R) It is because of the increasing calcium content downwards in arid soil.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and Rare true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
ASSERTION AND REASON BASED QUESTIONS
46. Assertion (A): Wind blows loose soil off from flat or sloping land is known as wind erosion.
Reason (R): Soil erosion is also caused due to defective methods of farming.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and Rare true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
47. Assertion (A): The laterite soil develops under tropical and sub-tropical climate with alternate wet and dry season.
Reason (R): This soil is formed by the depositional activity of the river.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
ASSERTION AND REASON BASED QUESTIONS
48. Assertion : Terrace cultivation does not restrict erosion.
Reason : Running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies which help us to cultivate crops.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) Both A and R are false.
49. Assertion : Land is a natural resource of utmost importance.
Reason : Land can be used only for agricultural purposes.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and Rare true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
ASSERTION AND REASON BASED QUESTIONS
50. Assertion : The availability of resources is not the only necessary condition for the development of any region.
Reason: Not only availability of resources but also corresponding change in technology is necessary for development of any region.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
51. Assertion : Controlling on mining activities doesn’t control land degradation.
Reason: In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, land degradation has occurred due to overgrazing, not mining.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision
SOURCE BASED QUESTIONS
52. Read the source and answer the following questions.
Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable can be termed as ‘Resource’.
The process of transformation of things available in our environment involves an interactive relationship between nature, technology and institutions. Human beings interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development. Do you think that resources are free gifts of nature as it assumed by many? They are not. Resources are a function of human activities. Human being themselves are essential components of resources. They transform material available in our environment into resources and use them.
(i) Which among the following can be counted as a resource?
(a) Livestock
(b) Wind mill
(c) Railway lines
(d) All of the above
(ii) When nature gets transformed in different ways, then which of the following takes place?
(a) Economic development
(b) Resource planning
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
(iii) Human beings interact with nature through which of the following?
(a) Institutions
(b) Resources
(c) Technology.
(d) None of these
53. Read the source and answer the following questions.
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow.
A few economists think that Indian farmers have a bleak future if they continue growing food grains on the holdings that grow smaller and smaller as the population rises. India’s rural population is about 600 million which depends upon 250 million (approximate) hectares of agricultural land, an average of less than half a hectare per person.
Indian farmers should diversify their cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops. This will increase incomes and reduce environmental degradation simultaneously. Because fruits, medicinal herbs, flowers, vegetables, bio-diesel crops like jatropha and jojoba need much less irrigation than rice or sugarcane. India’s diverse climate can be harnessed to grow a wide range of high-value crops.
I. which one of the following are not High value crops.
(A) Grapes and Guava
(B) Rice and Maize
(C) Jatropha and jojoba
(D) Rose and jasmine
II. Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) India’s climate do not support high value crops.
(B) Jatropha and Jojoba are beverage crops.
(C) Diversifying cropping pattern is profitable.
(D) High value crops need more water.
III. Why should farmers grow more of medicinal herbs and flowers?
(A) They increase farmers income.
(B) They need less irrigation.
(C) They reduce environmental degradation.
(D) All of the above.
IV. Which of the following statement is true in context of the given passage?
(A) Indian farmers produce more cereals.
(B) Indian farmers produces less high value crops.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
V. Why do economists think that Indian farmers have a bleak future?
(A) Because of ‘Right to inheritance’
(B) Becaude of ‘Diversification of cropping pattern.
(C) Because of India’s diverse climate
(D) All of these
VI. Why should Indian farmers diversify their cropping pattern?
(A) to increase income and reduce environmental degradation
(B) Because cereals are high value crops.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision
54. Read the source and answer the following questions.
Resource planning is a complex process which involves
(i) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
(ii) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
(iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
India has made concerted efforts for achieving the goals of resource planning right from the First Five Year Plan launched after Independence. The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of any region, but mere availability of resources in the absence of corresponding changes in technology and institutions may hinder development. There are many regions in our country that are rich in resources but these are included in economically backward regions. On the contrary there are some regions which have a poor resource base but they are economically developed.
(i) Why resource planning is necessary?
(a) For equal distribution of resource
(b) For conservation of resource for future generation
(c) To avoid further destruction of the Environment
(d) All of the above
(ii) In spite of having lot of natural resources, India’s development shows ……..
(a) advanced technology
(b) good availability of resources
(c) lack of resource planning
(d) All of the above
(iii) Why many regions of India are rich in resources but economically backward?
(a) Unequal distribution of resource
(b) Lack of resource planning
(c) Poor quality of resource
(d) Because of large population
(iv) Why certain regions despite having poor amount of sources are well developed?
(a) Region have better resource planning
(b) Unequal distribution of resources
(c) Region have less density of population
(d) good quality of resources
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision
55. Read the source and answer the following questions.
We live on land, we perform our economic activities on land and we use it in different ways. Thus, land is a natural resource of utmost importance. It supports natural vegetation, wildlife, human life, economic activities and transport and communication systems. However, land is an asset of a finite magnitude, therefore, it is important to use the available land for various purposes with careful planning. India has land under a variety of relief features, namely; mountains, plateaus, plains and islands. About 43 per cent of the land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry. Mountains account for 30 per cent of the total surface area of the country and ensure perennial flow of some rivers, provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects. About 27 per cent of the area of the country is the plateau region. It possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
(i) Land supports natural vegetation, wildlife and human population so land is ……… resource.
(a) Developed
(b) Potential
(c) Natural
(d) Man made
(ii) Careful planning of land resource in India is needed as ……….
(a) India has a variety of resources
(b) land is finite
(c) land is of utmost importance
(d) All of the above
(iii) Which of the following will not be a proper utilisation of land resource?
(a) Developing tourist places in mountains
(b) Constructing canals near perennial rivers
(c) Planting trees near mines
(d) Setting up industries on fertile land
(iv) The plateau region of India can be developed as……….
(a) Industries
(b) Extraction of minerals
(c) Both A and B
(d) None of these
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision
56. Read the source and answer the following questions.
Alluvial soil is the most widely spread and important soil. In fact, the entire Northern plains are made of alluvial soil. These have been deposited by three important Himalayan river systems-the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra. These soils also extend Rajasthan and Gujarat through a narrow corridor. Alluvial soil is also found in the Eastern coastal plains particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri rivers.
The alluvial soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay. As we move inlands towards the river valleys, soil particles appear some what bigger in size. In the upper reaches of the river valley i.e. near the place of the break of slope, the soils are coarse. Such soils are more common in piedmont plains such as Duars, Chos and Terai. Apart from the size of their grains or components, soils are also described on the basis of their age. According to their age alluvial soils can be classified as old alluvial (Bangar) and new alluvial (Khadar). The Bangar soil has higher concentration of kanker nodules than the Khadar soil. It has more fine particles and is more fertile than the Bangar.
(i) Which of the following is not correct statement about Alluvial Soil?
(a) It is most abundant type of soil in India
(b) Alluvial soil is generally fertile
(c) They are mostly found in the western coastal plains.
(d) They are classified as Khadar and Bangar.
(ii) Which of the following soil has the largest area covered in India?
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Black soil
(c) Laterite soil
(d) Forest soil
(iii) Alluvial soil is also known as
(a) Regur soil
(b) Khadar soil
(c) Bangar soil
(d) Both (b) and (c)
(iv) The Khadar soils are found in
(a) flood plains
(b) near the river bed.
(c) over plateau
(d) in the foot hills of mountains.
57. Fill in the blanks:
i) Resources are classified as renewable and Non renewable on the basis of ________________
ii) Resources which are surveyed and their quantity and quality have been determined for utilisation are known as _____________ resource.
iii) ____________ soil develops due to high temperature and evaporation.
iv) A land is said to be culturable waste land if it is left uncultivated for more than ————– agricultural years
v) The First International Earth Summit was held in the year ____________,
Fill in the blanks:
vi) ________ percentage of land is plains in India.
vii) Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs can be termed as resource, provided it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and ______________ acceptable.
vii) Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access these are known as _____________.
viii) ____________________ soil has self aeration capacity.
ix) The ____________ soil consists of sand, silt and clay.
x) ______________________ Soil is formed by intense leaching.
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision
MAP BASED QUESTIONS (MCQ’s)
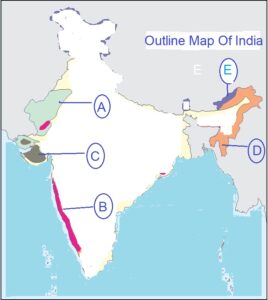
58. Features are marked in the given outline map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names.
Geography Revision Class X Term 1
A. These soils are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature.
B. The soil develops under tropical and subtropical climate with alternate wet and dry season in heavy rainfall areas.
C. They are well-known for their capacity to hold moisture and develop deep cracks during hot weather.
D. This soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau. .
E. These soils are found in the hilly and mountainous areas where sufficient water is available.
OPTIONS: (choose in correct sequence)
A. Arid soil, Alluvial soil, Black soil, Laterite soil, Montane soil.
B. Arid soil, Alluvial soil, Black soil, Red soil, Montane soil.
C. Arid soil, Red soil, Black soil, Laterite soil, Montane soil.
D. Arid soil, Laterite soil, Black soil, Red soil, Montane soil.
Q59. On the given political map of India, “A” and “B” are marked as Dams. Identify it from the following options.
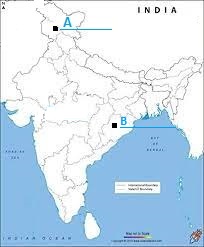
OPTIONS:
A. Salal and Sardar Sarovar
B. Salal and Rana Pratap Sagar
C. Tehri and Sardar Sarovar
D. Tehri and Rana Pratap Sagar.
Q60. Features are marked by numbers in the given outline map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map.
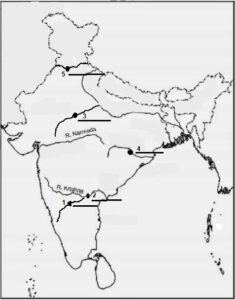
1. A dam constructed across the Tungabhadra river.
2. A dam on river Krishna.
3. A dam on river Chambal
4. Identify the dam constructed across Mahanadi river.
5. Identify the dam constructed across Satluj river.
OPTIONS: (choose in correct sequence)
A. Tungbhadra, Nagarjun Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar. Hirakud, Tehri.
B. Nagarjun Sagar, Tungbhadra, Sardar Sarovar, Hirakud, Bhakhra Nangal.
C.Tungbhadra , Nagarjun Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, Hirakud, Bhakhra Nangal.
D.Tungbhadra , Nagarjun Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar,Bhakhra Nangal , Tehri.
60 most expected Geography questions in Term I for revision for class X
Conclusion:
60 most expected Geography questions in term I for revision is prepared to give you a practice before appearing for the Term I exams. If you can solve more than 50 questions in 60 minutes correctly, you are likely to score full marks in Geography. Do not appear in board exams without solving these 60 most expected Geography questions. These 60 questions cover the entire syllabus prescribed by the board. The chapters are, Resources and Development, map work from all chapters Class 10 Term I Map MCQ’s – COMPLETE SYLLABUS and Agriculture MCQ’s.
Do solve 60 most expected Geography questions. Which question was the most difficult one for you ? Was these 60 most expected Geography questions helpful to you? Pl. write your opinion in the comment box.
All the best for your Term I Board exams.





0 Comments